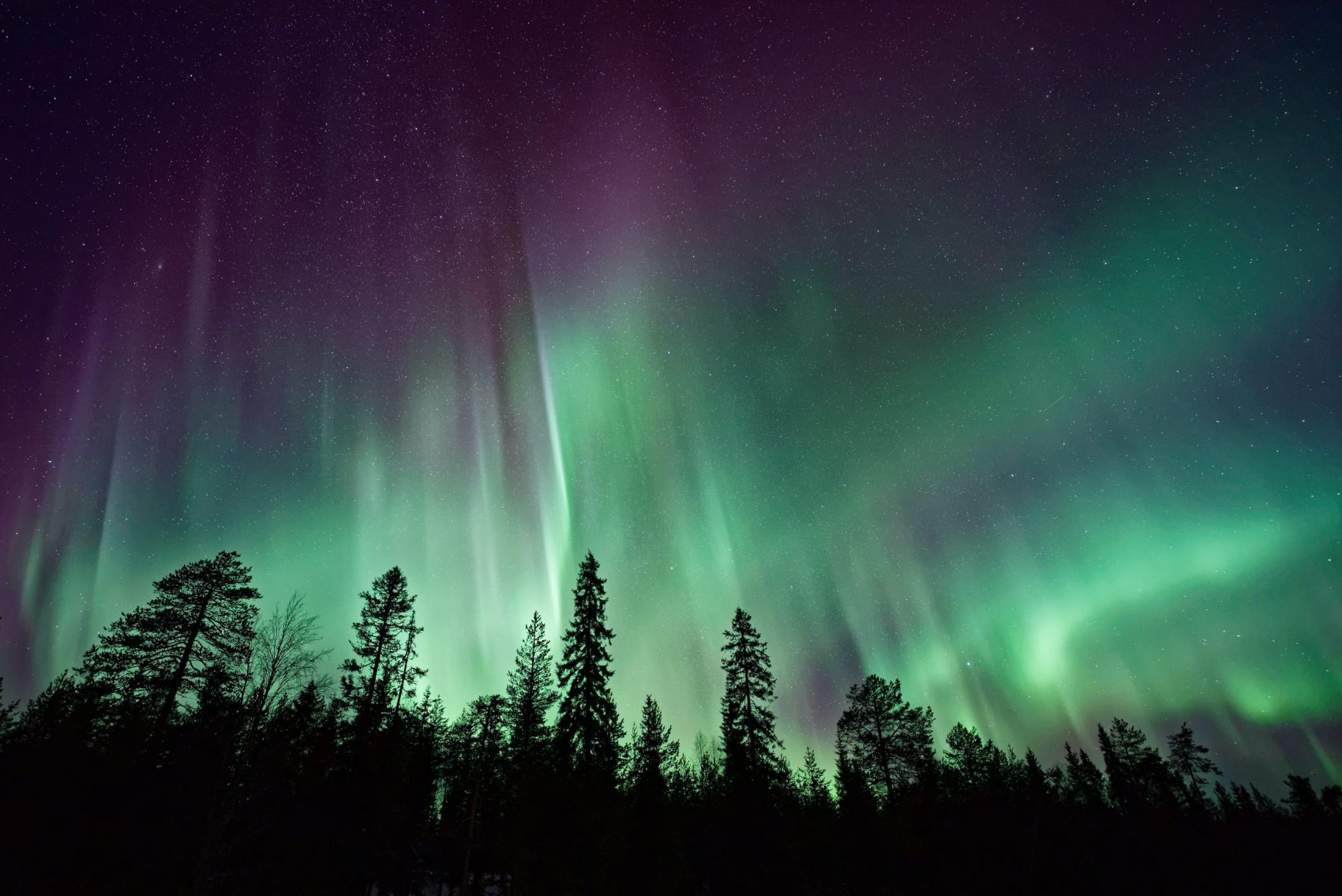
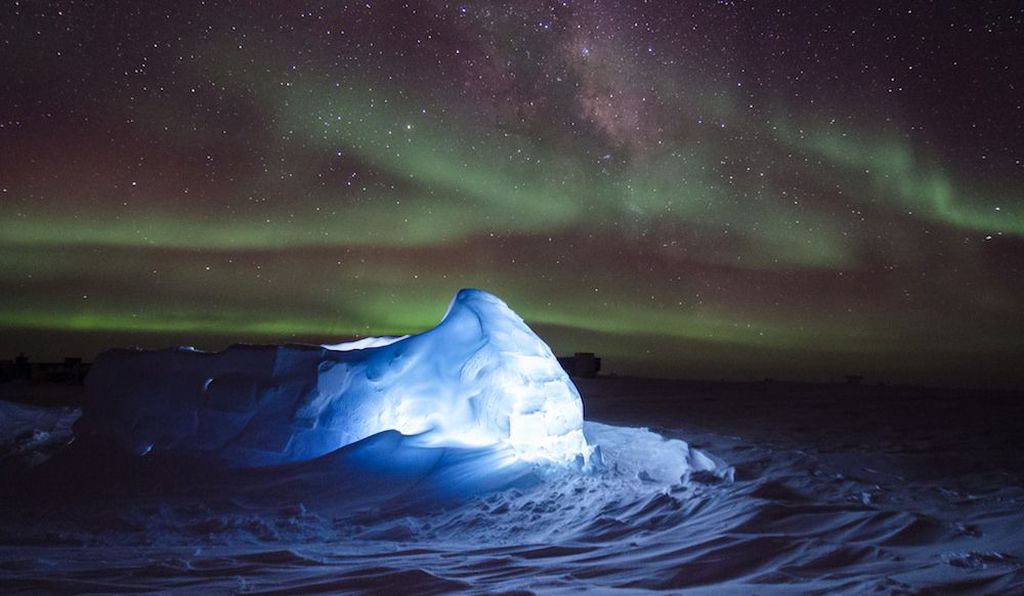
All of us have either seen (whether in a photo or real life) or heard of the Aurora Borealis, more commonly known as the northern lights. These spectacular lights are most commonly green in color but can turn purple and even red. So, what causes them, and why can you only see them in the far north?
The Science Behind the Northern Lights
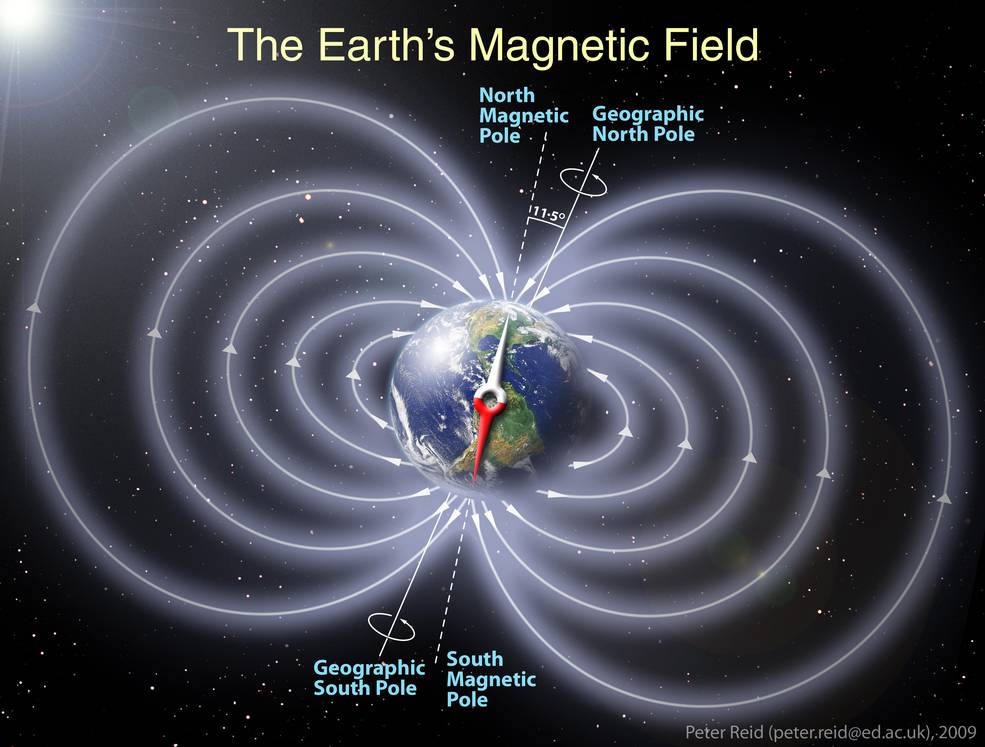
Two main factors need to be understood to explain why the northern lights appear: the earth’s magnetic field and the sun’s solar radiation.
In the simplest terms, the sun emits solar radiation, also known as solar wind, which constantly gets blasted at our earth. This solar radiation carries a lot of energy with it in the form of plasma. When this solar wind hits our earth’s atmosphere, it reacts with the common elements in our air, nitrogen, and oxygen. The byproduct of this reaction is excess energy in the form of radiation, which produces the visible light we call the northern lights.
So why can we only see them in certain places? This is where the earth’s magnetic field comes into play. When these solar winds hit the earth’s magnetic field, they follow the magnetic field’s path, which ends at each earth’s pole. Therefore, the amount of solar radiation hitting our earth is most dense in the poles, so we can only see the northern lights from close to the poles.
The amount of solar wind that hits our earth varies. When there is a low amount of solar wind hitting the earth, we refer to it as a period of low solar activity, and when there is a lot of solar wind, we refer to it as a period of high solar activity.
Where do You Have to Be to See the Northern Lights
The answer to this question is ever-changing as it depends on how high the solar activity is in a given period. In general, it is said that you want to be at least 66º north in latitude to have a good chance at seeing them. However, there have been many times northern lights have been visible much further south. In fact, in September 1859, during the strongest geomagnetic storm ever recorded, the northern lights were as visible as far south as Cuba!
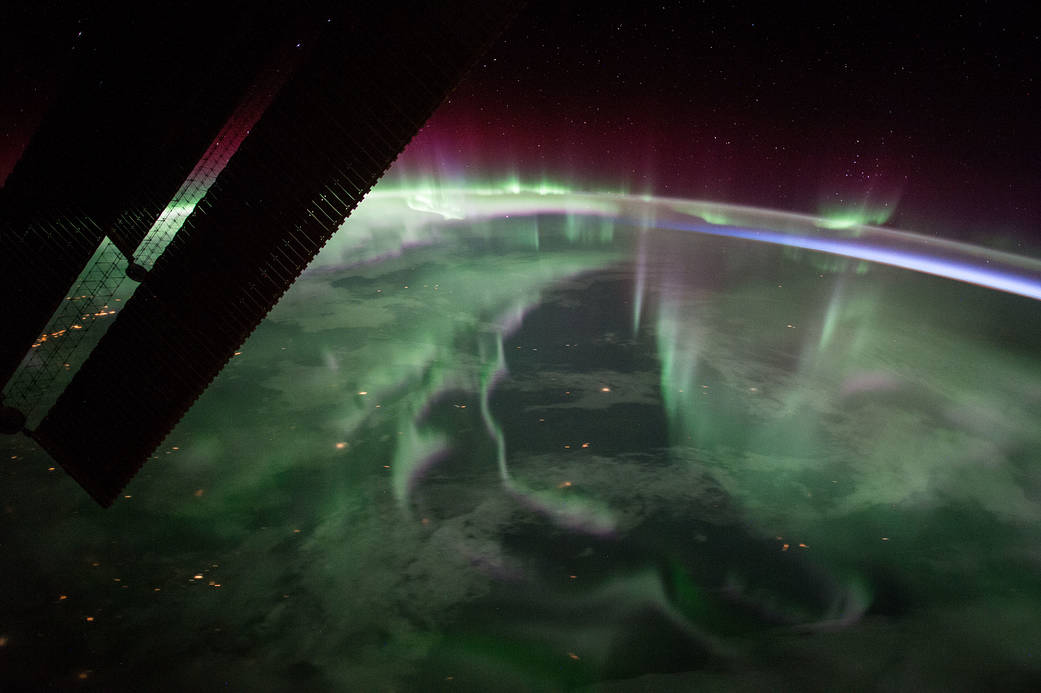

Southern Lights?
Although the northern lights are much more famous than the southern lights, they both do indeed exist (hence why the scientific name is not northern lights but rather auroras). The northern lights get much more attention and are much more famous because they are much easier to see. If you are interested in seeing the southern lights, you either need to be in Antarctica or, if you are lucky, from New Zealand or Australia’s southern tips.
Effects of the Northern Lights
In extreme cases, solar radiation, which is how the northern lights are formed, can severely affect our modern electrical grid. When a high amount of solar radiation hits the earth’s magnetic field, this is known as a geomagnetic storm. The changing magnetic field energy can induce currents in our modern electric grid, triggering blackouts. An example of this occurred in 1989 in Quebec, Canada, when a large geomagnetic storm triggered a blackout that left six million people in the dark.





