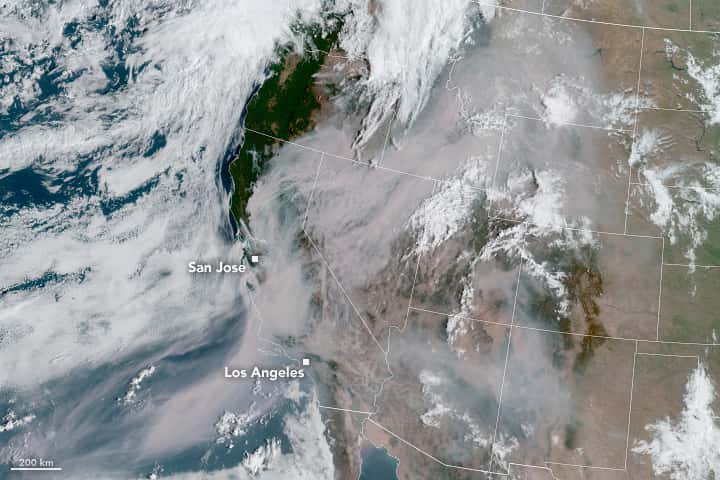
Almost 100 uncontrolled large fires across the western US are creating huge clouds of smoke affecting the air quality as far east as Kansas and the Great Plains. The smoke could soon spread into the southeast.
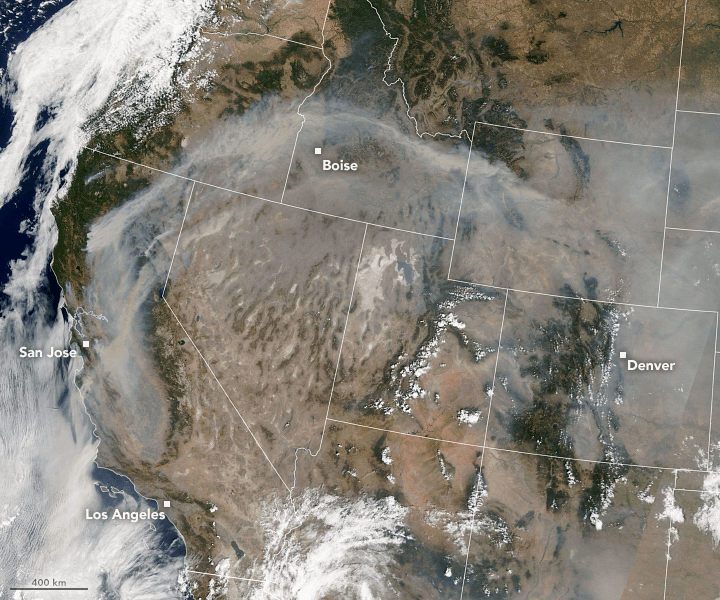
Fires in California, Colorado, Oregon, and other western states have forced tens of thousands of people to be evacuated, with the smoke in the atmosphere affecting millions. Not what you want to hear in the middle of a respiratory pandemic. Early research suggests that smoke inhalation could make the coronavirus worse.
The majority of the smoke is coming from California, where more than 10,000 lightning strikes in a 72-hour period sparked fires that, exacerbated by the heatwave, have contributed to the burning of more than 1.5-million acres.
“This amount of smoke is extremely unusual. The amount of smoke is due to both the large number of individual fires, as well as large ‘fire complexes,’ which are extremely large fires.”
– Michael Garay, an air quality researcher at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory
NASA researcher Ryan Stauffer reports that a monitoring station east of Los Angeles recorded the highest ozone levels seen anywhere in the country since 2007. And the air quality in Denver is currently the equivalent of smoking two cigarettes a day.
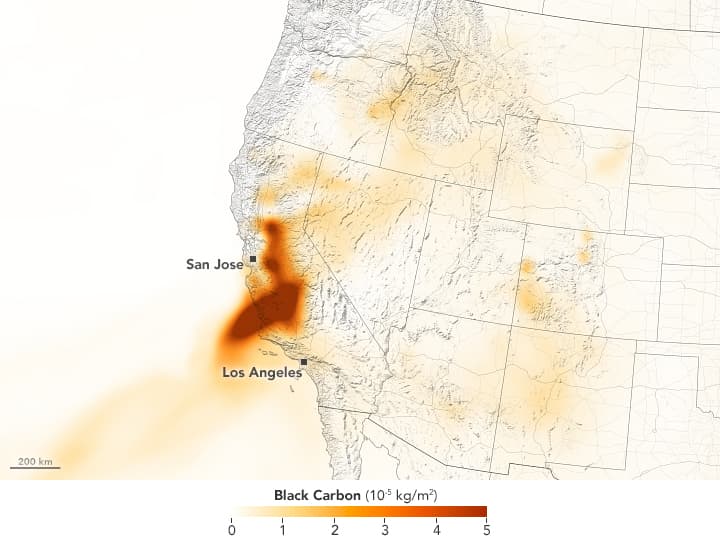
The area around San Luis Obispo, between Los Angeles and San Francisco, had some of the worst air quality in the world on Friday.






killa cali