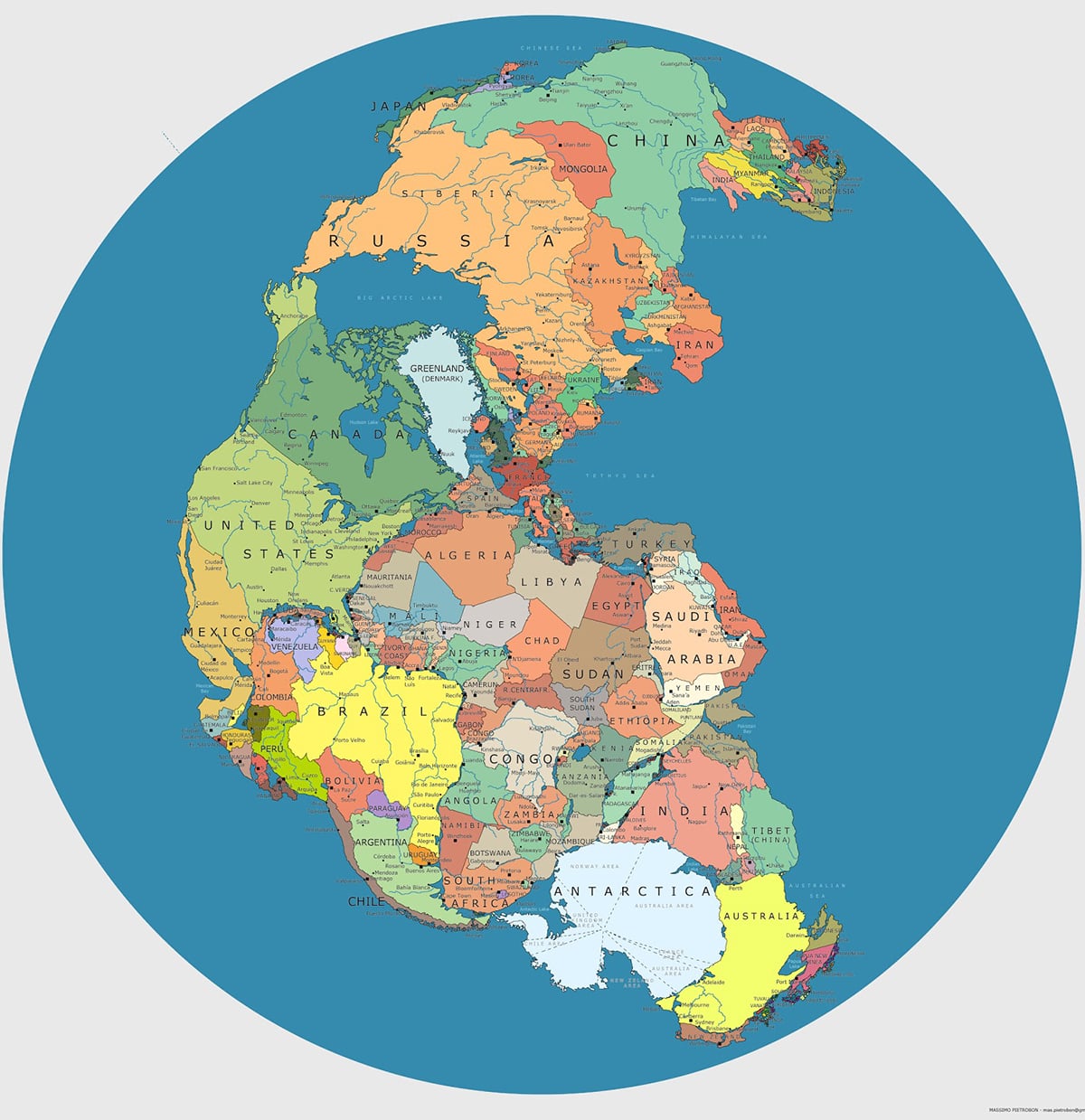
A map has been created overlaying modern countries on Pangea. Pangea is the last supercontinent to have formed on Earth. Pangea formed 300 million years ago and was a solid landmass surrounded by ocean.
The ocean surrounding Pangea is called Panthalassa, which means “all sea” in greek. This ancient superocean occupied 70% of Earth’s surface. Most of the oceanic plates of Panthalassa have been consumed by subduction, which means that the oceanic tectonic plates have been pushed down into Earth’s mantle by other tectonic plates. Panthalassa was a hemisphere-sized ocean. It is believed to have had relatively simple ocean currents because of its size.
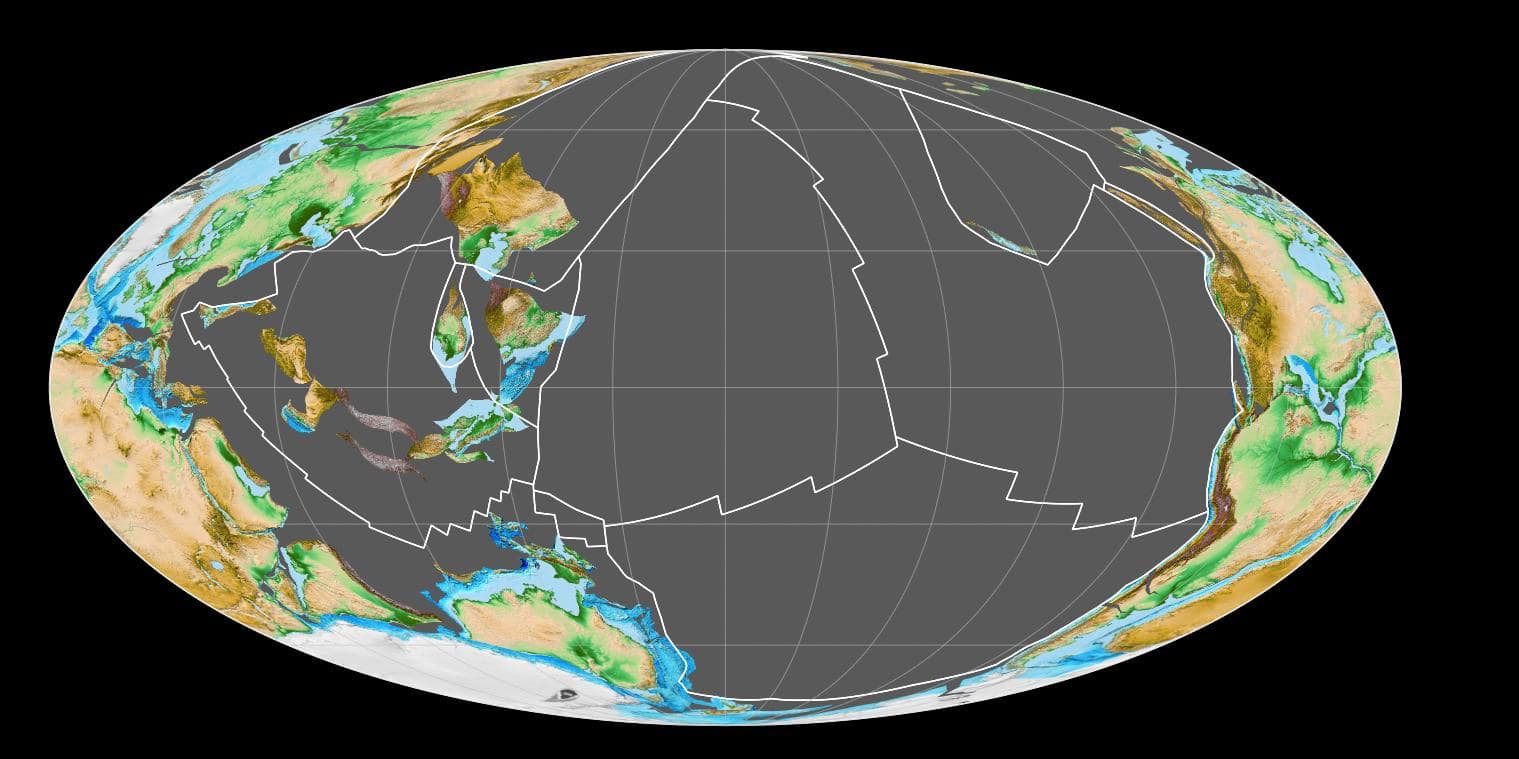
Pangea was Earth’s most recent supercontinent. Previous supercontinents include Pannotia, Rodinia, and Columbia, which is also called Nuna. The first supercontinent thought to exist is called Vaalbara, which contained the Superior Craton. A craton is an area of Earth’s crust that has been stable and relatively unchanged for long periods of time. The Superior Craton is located in North America and covers central Canada as well as Quebec and areas of Minnesota and the Dakotas.
There are many pieces of evidence that support the past existence of Pangea, including the presence of fossils of similar or identical species on different continents. Additionally, eastern South America and Africa’s west coast are very geologically similar. Furthermore, paleomagnetic studies support the existence of Pangea.

Pangea broke apart in three distinct phases. First, rifting occurred between what is now North America and Africa. This created the north Atlantic Ocean. Second, a supercontinent broke into what is now modern-day Africa, India, South America, Australia, and Antarctica. Finally, North America and Greenland separated from Eurasia.
In the future, a new supercontinent is likely to form. Australia is moving north, towards Asia. India is already colliding with Asia, which has created the Himalaya mountains. Meanwhile, Africa will continue moving north.
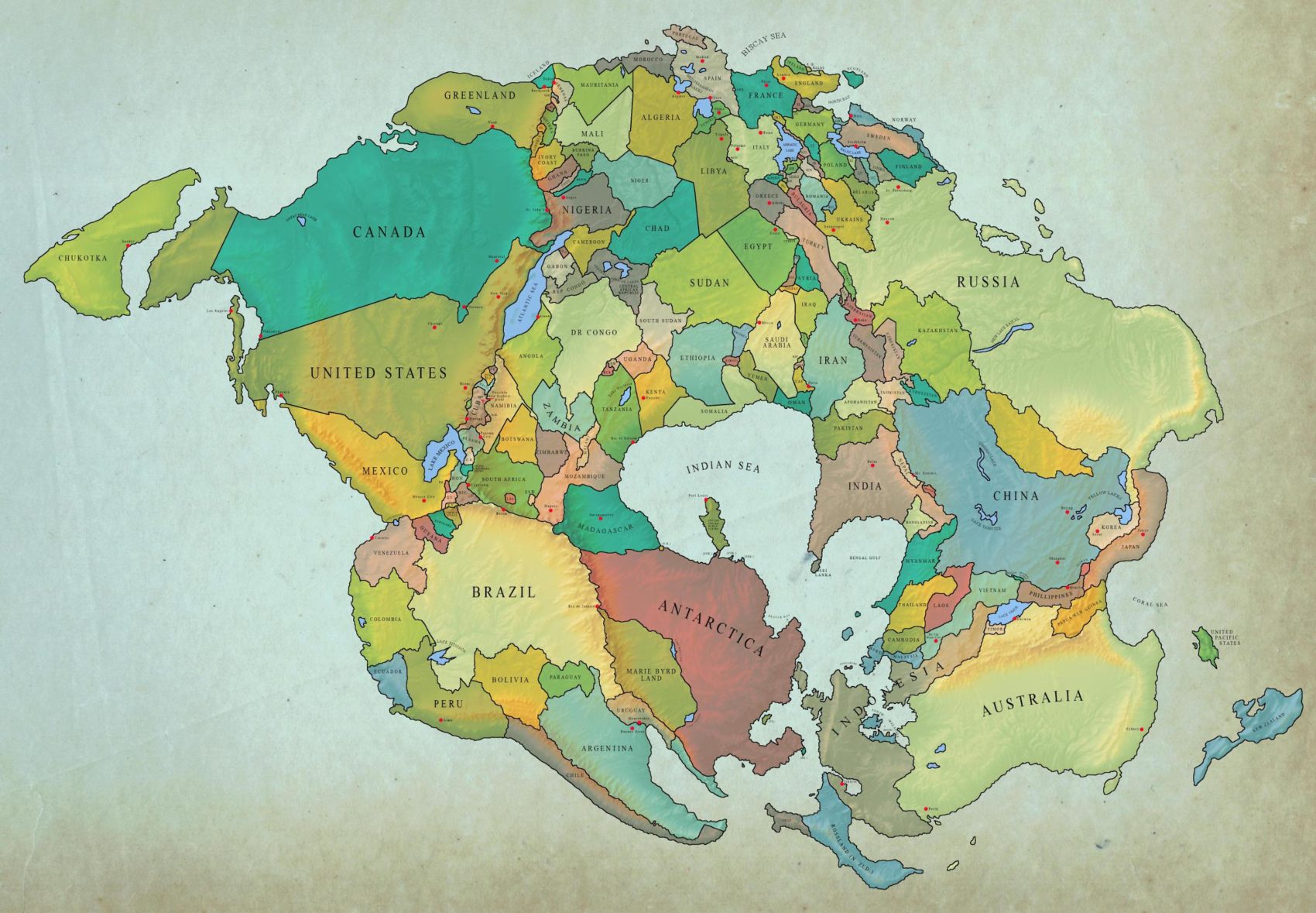
The Atlantic ocean will continue to widen until a new subduction zone forms, at which point the Atlantic ocean will begin to shrink as the Americas set off on a collision course with Africa/Europe. The collision between the Americas and Africa/Europe is likely to create mountains similar to the modern Himalayas. In 250 million years, Earth will be a very different looking place.




